Helpshift APIs
Helpshift APIs
Helpshift provides a way to use each functional element of the SDK separately based on your requirements. You can call only specific screens from the SDK based on the functionality you want to expose in your app.
There are 6 different ways in which the Helpshift SDK can be presented in your app.
Integrating Contact Us & In App Messaging
Example: Support.showConversation(MyActivity.this); where MyActivity.this is the Activity you're calling Helpshift from
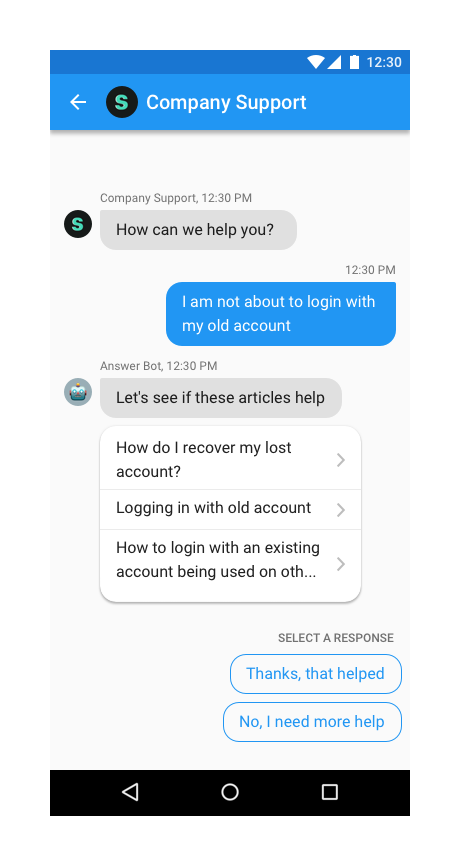
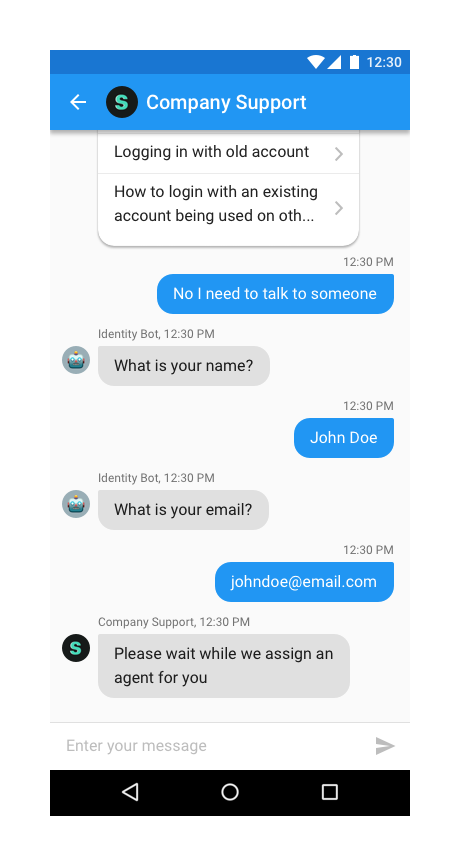
You can use the API call Support.showConversation(MyActivity.this);
to provide a way for the user to send feedback or start a new conversation
with you. This has been provided if you want to embed a "Send
Feedback" or "Contact Us" action in your app and want to lead the
user to this action directly without having to go to the FAQ. Once, a
user starts a new conversation, this API call will show the conversation
activity. The conversation will ensue until it is resolved (and the
resolution is accepted by the user) or rejected by the agent.
Applicable to SDK version 3.10.0 and above.
Integrating FAQs
Example: Support.showFAQs(MyActivity.this); where MyActivity.this is the Activity you're calling Helpshift from
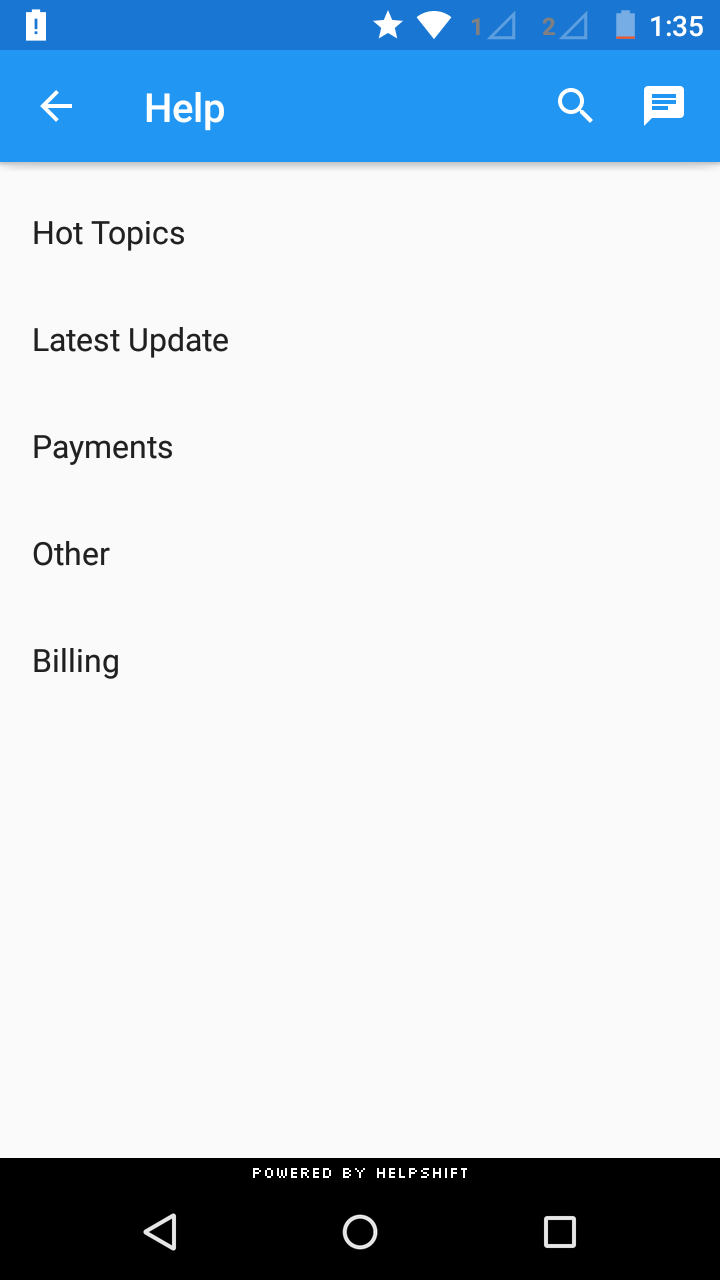
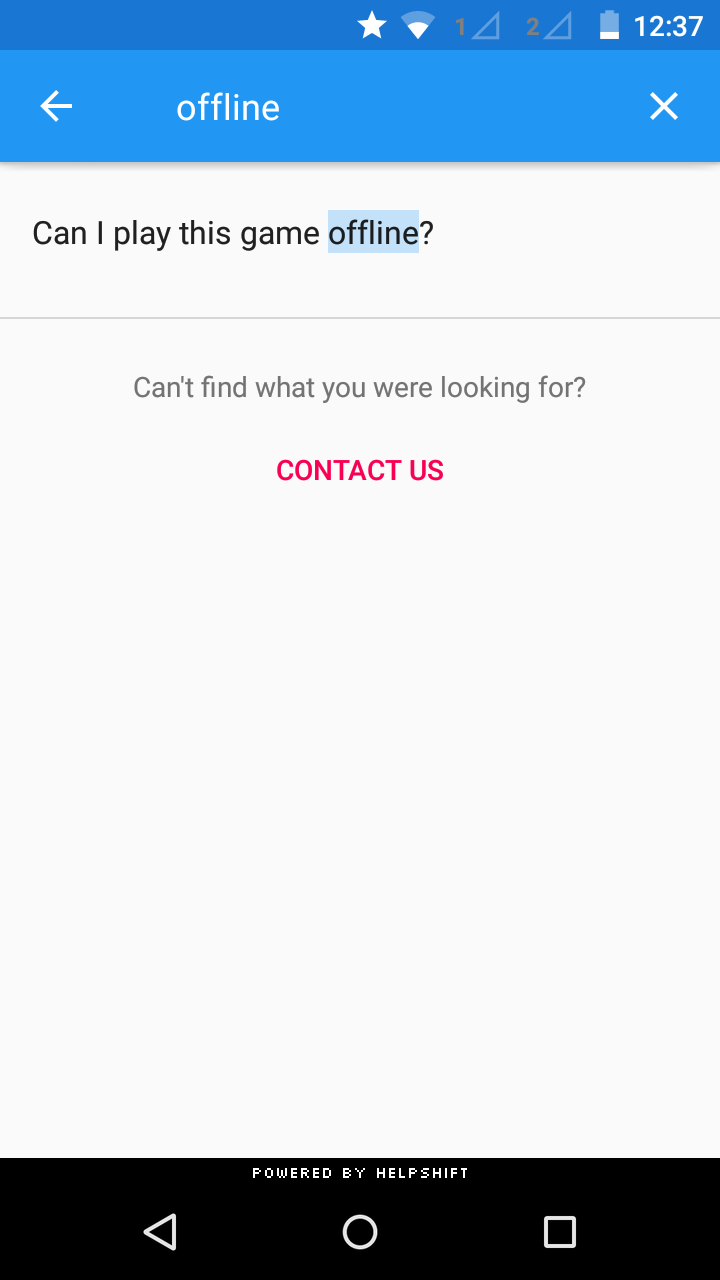
You can use the API call Support.showFAQs(Activity a) to provide a way for the user to invoke the purpose built help/support section in your app. This is the easiest approach to enable help in your app as it bundles all the capabilities of the Helpshift SDK in a simple and intuitive interface.
You can wire this API call to a "Help" or "Support" action in your app. This Activity combines the FAQ, Search and Contact Us functionality together in a single interface. In this view a user has to search for a specific question in the FAQ failing which they can report an issue. When you respond back to their question from the Helpshift Agent Dashboard, the reply will be shown as a count besides Contact Us, clicking on which will open up the conversation.
Check out SDK Configuration for more.
FAQ Filtering by tags
Starting v3.11.0 onwards, we have introduced FAQ filtering capability by tags. With the goal of helping the end user see focused & related content e.g. basis the user demographic or device profiles, developers can now choose the new capability for FAQ filtering and showing a focused FAQ list to the right audience. Typical cases why you would want to use FAQ filtering are :
- You want to show specific FAQs for specific audience. E.g. if you may categorize the users as ‘beginner’, ‘intermediate’ or ‘expert’ based on your business logic
- You may want to show specific FAQs based on the device. E.g. a set of FAQs for Tablet vs. Phone
FAQ filtering is a 2 step approach
- FAQs need to be classified using the issue tags field on the dashboard e.g. tags ‘phone’ & ‘tablet’.
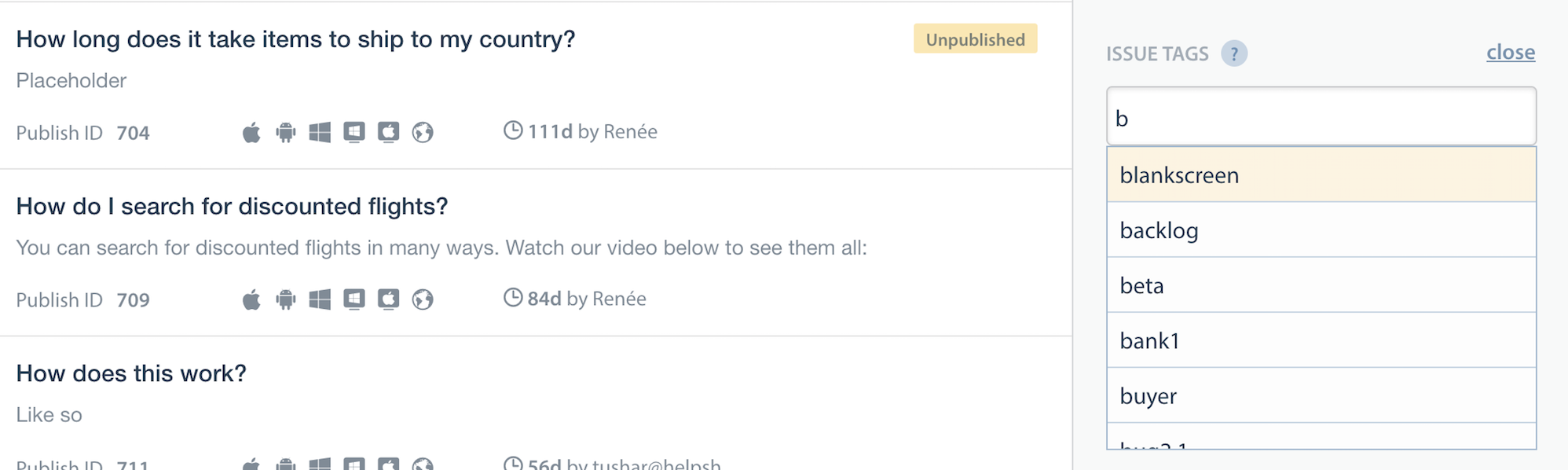
- Once the FAQs are tagged, they can be filtered at the SDK using the filter options described here.
Helpshift has 2 types of tags mainly Issue Tags & Search Tags.
- Issue tags are used to filter the FAQ list on the SDK with the filter rules.
- Search tags (a.k.a Search Keywords) When performing in-app search, Helpshift SDK gives preference to these keywords. You can also use this to add alternative keywords that users might search for, but which may not exist in the FAQ title or the content.
How to use FAQ filtering
This will be a config option which will be supported by the showFAQs and showFAQSection APIs.
Usage :
- Using ApiConfig
- Using Map
String operator = FaqTagFilter.Operator.AND / FaqTagFilter.Operator.OR / FaqTagFilter.Operator.NOT;
String[] filterTags = new String[]{"tag1", "tag2"};
FaqTagFilter faqTagFilter = new FaqTagFilter(operator, filterTags);
ApiConfig apiConfig = new ApiConfig.Builder()
.setWithTagsMatching(faqTagFilter)
.build();
The withTagsMatching option will take a FaqTagFilter object which takes two parameters
- operator : one of
FaqTagFilter.Operator.AND,FaqTagFilter.Operator.OR,FaqTagFilter.Operator.NOTwhich will serve as conditional operators for the given tags (String). - tags : the actual tags in the query (String Array)
Example :
//If the developer wants to show all FAQs with tags “android-phone” or “android-tablet”
String operator = FaqTagFilter.Operator.OR;
String[] filterTags = new String[]{"android-phone", "android-tablet"};
FaqTagFilter faqTagFilter = new FaqTagFilter(operator, filterTags);
ApiConfig apiConfig = new ApiConfig.Builder()
.setWithTagsMatching(faqTagFilter)
.build();
Support.showFAQs(MyActivity.this, apiConfig);
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
String operator = "and/or/not";
String[] filterTags = new String[]{"tag1", "tag2"};
map.put("operator", operator);
map.put("tags", filterTags);
HashMap config = new HashMap();
config.put("withTagsMatching", map);
The withTagsMatching option will be a HashMap containing 2 keys
- operator : one of “and”, “or”, “not” which will serve as conditional operators for the given tags (String).
- tags : the actual tags in the query (String Array)
Example :
//If the developer wants to show all FAQs with tags “android-phone” or “android-tablet”
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
String operator = "or";
String[] filterTags = new String[]{"android-phone", "android-tablet"};
map.put("operator", operator);
map.put("tags", filterTags);
HashMap config = new HashMap();
config.put("withTagsMatching", map);
Support.showFAQs(MyActivity.this, config);
Showing a Particular FAQ Section
Example: Support.showFAQSection(MyActivity.this, "11"); where MyActivity.this is the Activity you're calling Helpshift from and "11" is the FAQ section publish-id

You can use the API call Support.showFAQSection(Activity a, String sectionPublishId) to show faqs from a particular FAQ section.
You'll need the publish-id of the section in this case:
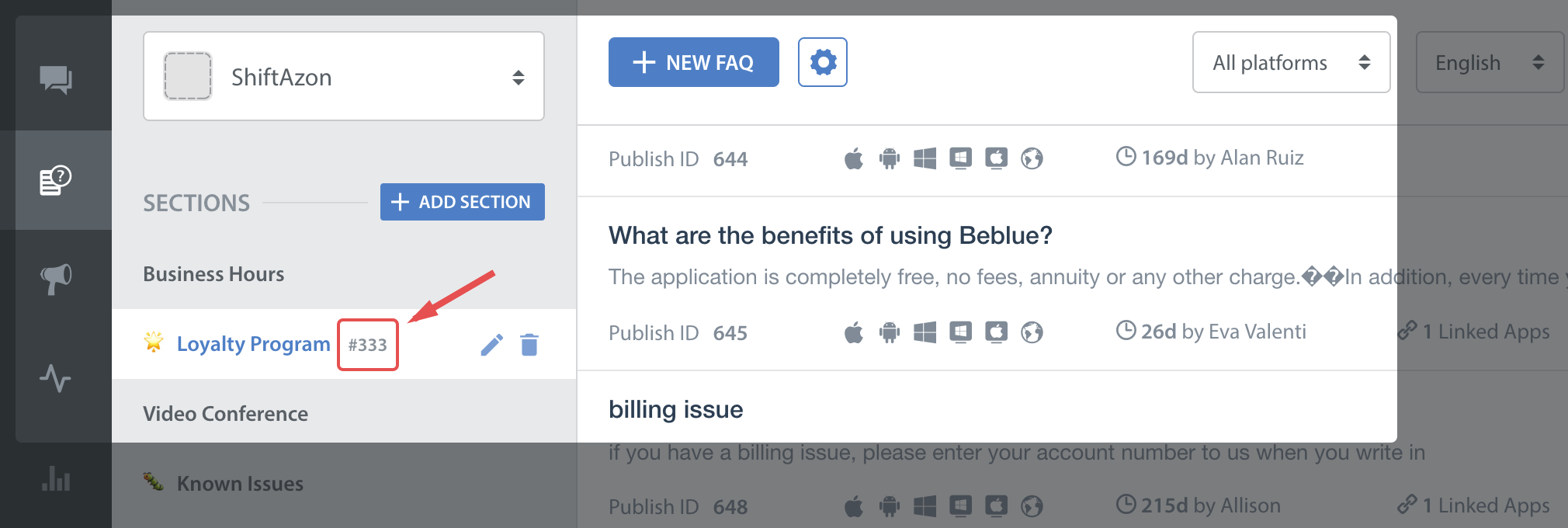
This feature works like a permalink for displaying specific FAQ sections as context sensitive help in your app. For example, if your app requires the user to login to using email, facebook and twitter, you could wire a help action on the login screen that can link to the Helpshift FAQ section called "Login help" which has several questions related to login methods.
Check out SDK Configuration for more.
Showing a Particular FAQ Question
Example: Support.showSingleFAQ(MyActivity.this, "51"); where MyActivity.this is the Activity you're calling Helpshift from and "51" is the FAQ publish-id
You can use the API call Support.showSingleFAQ(Activity a, String questionPublishId) to show a single faq question.
You'll need the publish-id of the FAQ in this case:
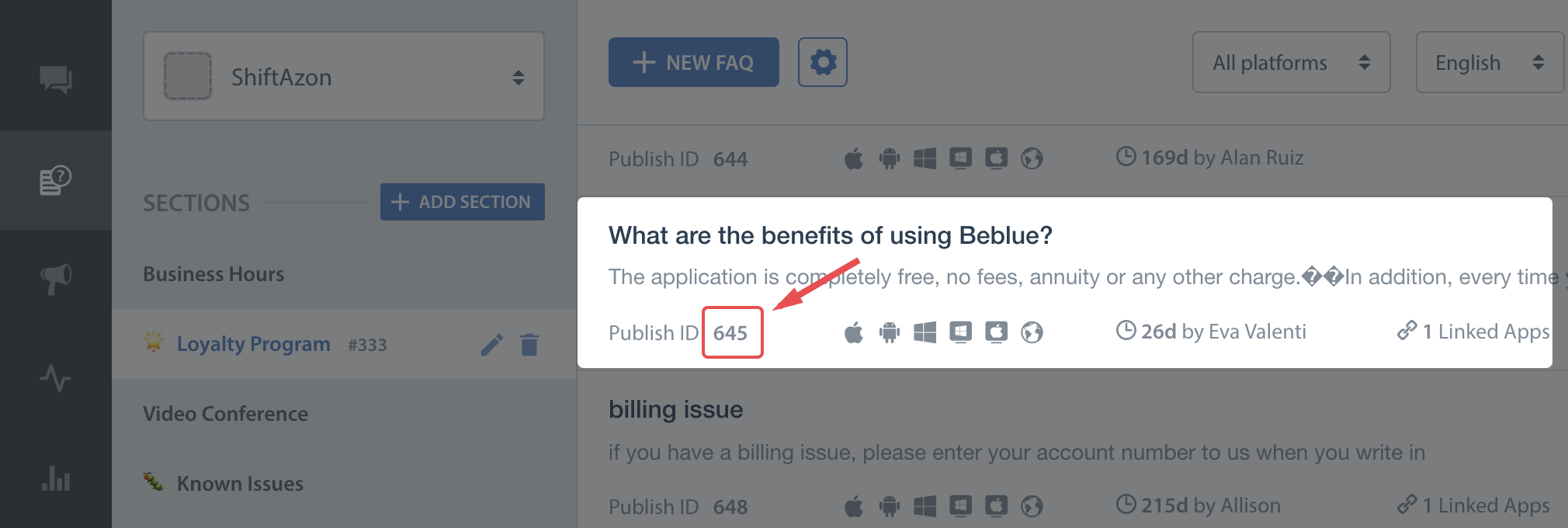
Check out SDK Configuration for more.
Guided Issue Filing
Applicable to version 4.1.0 and above.
Guided issue filing is a feature to capture more context when a user interacts with Helpshift Support. For example, lets say you want the user to file a ticket in case of a complaint and also in case he want to suggest a feature. With guided issue filing, you will be able to distinguish between these two use cases and take required actions (like assigning appropriate agents).
Guided Issue Filing can be achieved using Dynamic Forms.
Dynamic Forms also enable better FAQ discovery. Lets say there is a frequently viewed FAQ or FAQ section buried deep in your FAQ hierarchy. Some users might miss it out and opt to file an issue instead. With dynamic forms, you can create a new section (like top FAQs) that links to that FAQ section. Or create and alternate title to an FAQ (like 'How do I pay for gems' instead of 'Billing').
Dynamic Forms are built using one or more Flow types.
The app configures a dynamic form using 'flows'. There are 6 types of flows:
Flow to show conversation screen
new ConversationFlow(int titleStringResId, ApiConfig config)- similar to the showConversation: API
Flow to show all FAQs
new FAQsFlow(int titleStringResId, ApiConfig config)- similar to the showFAQs: API
Flow to show a FAQ section
new FAQSectionFlow(int titleStringResId, String sectionPublishId, ApiConfig config)- similar to the showFAQSection: API
Flow to show a single FAQ
new SingleFAQFlow(int titleStringResId, String questionPublishId, ApiConfig config)- similar to the showSingleFAQ: API
Flow to show a nested Dynamic form
new DynamicFormFlow(int titleStringResId, List<Flow> nextDynamicFormFlowList)
Flow to perform a custom action
For Example,
import com.helpshift.support.flows.Flow;
...
public class CustomFlow implements Flow {
private final int labelResId;
private final Activity activity;
public CustomFlow(int labelResId, Activity activity) {
this.labelResId = labelResId;
this.activity = activity;
}
@Override
public int getLabelResId() {
return labelResId;
}
@Override
public void performAction() {
Intent settingsActivity = new Intent(activity, UserSettingActivity.class);
activity.startActivity(settingsActivity);
}
}
Each flow needs a display text. This will be the text that will be displayed in the list item. It has to be localized String resource . Some flows also expect a 'config' Map. This will be the config that is passed to the subsequent Helpshift Support API. For example any config you wish apply to the conversation screen needs to be passed to the ConversationFlow(int titleStringResId, Map config)API. This is also where you will add your custom HSTags. These APIs do not add any custom meta data by default. You need to add your custom meta data including HSTags at your own.
The app can create any number of flows. These flows are then grouped into a dynamic form and displayed in a list view. There are two ways to display a dynamic form:
Launch a new activity to show the Dynamic Form Screen.
Support.showDynamicForm(@NonNull Activity activity, @NonNull String title, @NonNull List<Flow> flowList)
Get an embeddable Fragment to show in your activity (for eg. you can use this in your Navigation Drawer to replace the current fragment)
Support.getDynamicFormFragment(@NonNull Activity activity, @NonNull String title, @NonNull List<Flow> flowList)
Each dynamic form needs :
- Title: This will be the title displayed on the action bar
- flows: An List of supported Flow objects as discussed above.
Embeddable Support Fragments
Applicable to version 4.1.0 and above.
Helpshift now supports embeddable SupportFragments which can be used to embed a Helpshift support view inside your application's Activity. These support fragments can also be configured by providing a config map just like the previous Helpshift show-support-APIs. You need to complete the following steps to embed Helpshift fragments in your Activity :
Make sure that the Activity holding Helpshift's Embeddable fragments is extended from AppCompatActivity only.
Inherit theme of your Activity from one of the Helpshift's themes: Helpshift.Theme.Light.DarkActionBar, Helpshift.Theme.Light, Helpshift.Theme.Dark or Helpshift.Theme.HighContrast.
Create a style named Helpshift.Theme.Base and set its parent to your Activity's theme.
For Example,
<style name="YourActivityTheme" parent="Helpshift.Theme.Light.DarkActionBar">
<item name="colorAccent">@color/your_custom_color</item>
<item name="colorPrimary">@color/your_custom_color</item>
<item name="colorPrimaryDark">@color/your_custom_color</item>
</style>
<style name="Helpshift.Theme.Base" parent="YourActivityTheme"/>In your AndroidManifest.xml set the Activity theme (which contains the embeddable fragment) to Helpshift.Theme.Activity; which now contains both YourActivityTheme and the theme required by Helpshift embeddable fragments.
For Example,
<activity
android:name=".YourActivity"
android:theme="@style/Helpshift.Theme.Activity"/>
Following is the list of supported APIs :
All FAQs
Support.getFAQsFragment(Activity activity, ApiConfig config);Support.getFAQsFragment(Activity activity, Map config);Support.getFAQsFragment(Activity activity);Conversation
Support.getConversationFragment(Activity activity, ApiConfig config);Support.getConversationFragment(Activity activity, Map config);Support.getConversationFragment(Activity activity);Single section
Support.getFAQSectionFragment(Activity activity, String sectionPublishId, ApiConfig config);Support.getFAQSectionFragment(Activity activity, String sectionPublishId, Map config);Support.getFAQSectionFragment(Activity activity, String sectionPublishId);Single FAQ
Support.getSingleFAQFragment(Activity activity, String questionPublishId, ApiConfig config);Support.getSingleFAQFragment(Activity activity, String questionPublishId, Map config);Support.getSingleFAQFragment(Activity activity, String questionPublishId);Dynamic Form
Support.getDynamicFormFragment(Activity activity, String title, List<Flow> flowList, ApiConfig config);Support.getDynamicFormFragment(Activity activity, String title, List<Flow> flowList, Map config);Support.getDynamicFormFragment(Activity activity, String title, List<Flow> flowList);Support.getDynamicFormFragment(Activity activity, List<Flow> flowList, ApiConfig config);Support.getDynamicFormFragment(Activity activity, List<Flow> flowList, Map config);Support.getDynamicFormFragment(Activity activity, List<Flow> flowList);
Example :
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.fragment_container, Support.getFAQsFragment(this, config));
fragmentTransaction.commit();
When using SupportFragments with a standalone toolbar (i.e. toolbar which is a standalone widget and not used as an action bar) pass your toolbar id in the config map with the "toolbarId" key.
SupportFragments can only be embedded inside Activities and not fragments.
Handling onBackPressed with Helpshift's Embeddable Fragments
There is an issue with Android where onBackPressed doesn't behave as
expected when used with nested fragments. Use the following guidelines for
handling onBackPressed behaviour:
Override
onBackPressedinside your parent activity which contains the Helpshift'sSupportFragment.If the fragment is Helpshift's
SupportFragment, call SupportFragment'sonBackPressedmethod which return a boolean value. If back press was handled by Helpshift's SupportFragment, this method will return valuetrue. If there is nothing to go back in, this method will return valuefalse, in which case you can either pop the SupportFragment orfinishthe activity as per your requirements.
For Example:
public void onBackPressed() {
List<Fragment> fragments = getSupportFragmentManager().getFragments();
if (fragments != null) {
for (Fragment fragment : fragments) {
if (fragment != null
&& fragment.isVisible()
&& fragment instanceof SupportFragment) {
if (((SupportFragment) fragment).onBackPressed()) {
return;
} else {
FragmentManager childFragmentManager = fragment.getChildFragmentManager();
if (childFragmentManager.getBackStackEntryCount() > 0) {
childFragmentManager.popBackStack();
return;
}
}
}
}
}
super.onBackPressed();
}
Handling language change with Helpshift's embeddable fragments
If you are using Helpshift SDK's setSDKLanguage API on devices with Android API level 25 and above, then use the following guidelines to update the Helpshift SDK's locale:
- Override
attachBaseContextmethod inside your activity which contains Helpshift's embeddable fragment. - Create a new Context with resources configured with required language code and pass the updated context to the Activity via
attachBaseContext.
Refer to the sample code provided:
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context context) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 17) {
Locale locale = new Locale("<LANGUAGE CODE>", "<COUNTRY CODE>");
Resources res = context.getResources();
Configuration config = new Configuration(res.getConfiguration());
config.setLocale(locale);
context = context.createConfigurationContext(config);
}
super.attachBaseContext(context);
}
This language handling is required because of the following changes in the Android:
- From Android API level 17,
Context.createConfigurationContext()API is introduced to create custom configuration context object. - From Android API level 25,
Resources.updateConfiguration()API is deprecated and it is recommended to useContext.createConfigurationContext()which will create a new context instead of updating the old context object. [Reference](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/res/Resources.html#updateConfiguration(android.content.res.Configuration, android.util.DisplayMetrics))
Enabling hardware acceleration in Manifest
There are some known issues in rendering the FAQ fragment views if hardware acceleration is explicitly disabled for the application (the system enables it by default) due to known WebView issues on Android 5.1. Thus, Helpshift recommends you to enable hardware acceleration in your app. However, if you want to disable hardware acceleration in your app, you can enable it only for the activity in which you plan to attach the SDK's fragments. For example, in your AndroidManifest.xml:
<!-- (optional) if you want to keep hardwareAcceleration as false for you app -->
<application
android:hardwareAccelerated="false">
...
<activity
android:name="<com.example.HelpshiftHostActivity>"
android:hardwareAccelerated="true" />
</application>