Notifications
Configure Push and In-app notifications.
All the public APIs in the SDK should be called after initializing the SDK via Helpshift installWithPlatformId API
Notifications can be sent to your users when:
- You or your support agents reply to an issue submitted by them
- You send a Proactive Engagement notification targeting the user
Setting push notifications involves configuring both the Helpshift admin dashboard as well as the client app.
Configure push notifications in the Helpshift admin dashboard
Configure Helpshift's push notification service in the Helpshift admin interface
To enable the Helpshift system to send push notifications to your users you will have to add iOS as a platform in your app (if you have not added already). And then click on the push notifications option.
In order to send push notifications to all iOS mobile apps and games, you need to establish an authenticated connection with the Apple Push Notification Servers (APNs). There are two methods you can use to authenticate:
- The newer token-based method (.p8)
- The older certificate-based method (.p12)
Token-based method (.p8)
The token-based method is faster because it offers a stateless way to communicate with APNs. It doesn't require APNs to look up the certificate or any other information related to the provider server.
We now support the newer token-based .p8 key method, which allows you to send notifications to all your iOS apps and games using a single key. You can generate your .p8 key through your Apple developer account, as explained here.
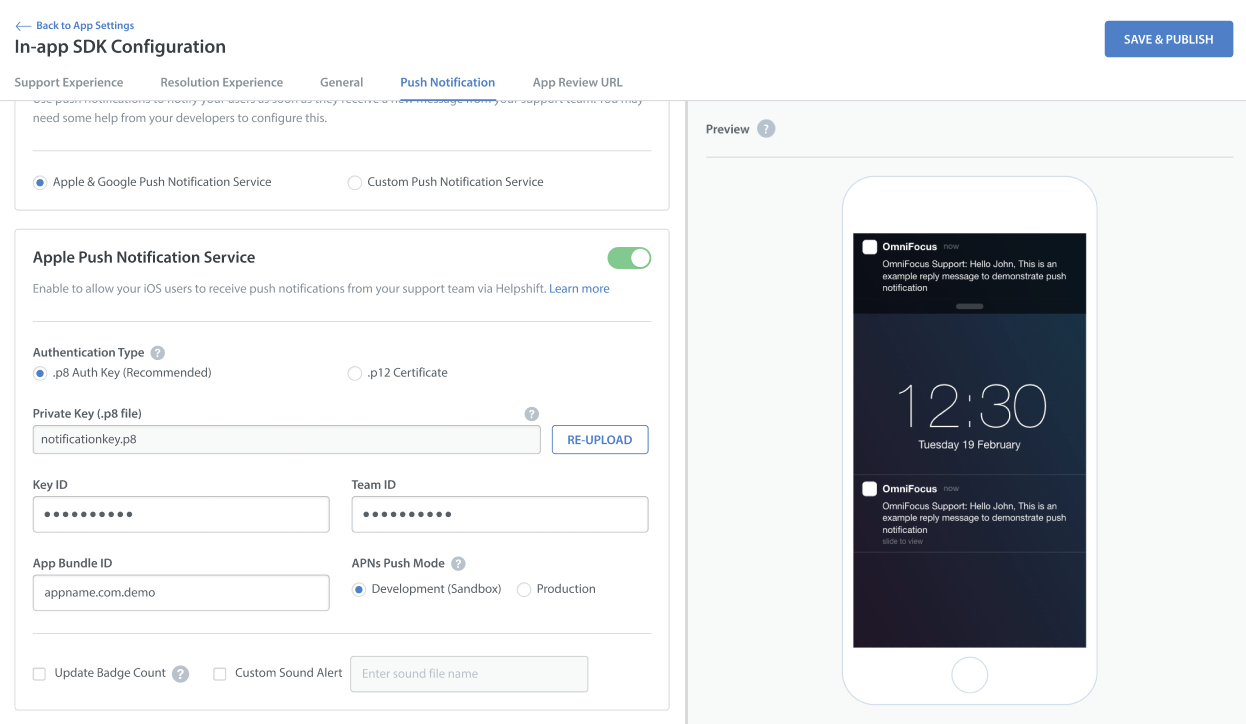
Here are the steps to configure iOS push notifications using .p8 keys:
Go to Settings, then navigate to the APP SETTINGS section to choose the app you want to configure.
On the App settings page, click on the CONFIGURE option next to In-app SDK.
On the In-app SDK Configuration page, navigate to the Push Notification section.
Enable the toggle for Apple Push Notification Service if not enabled. The app selects the p8 key authentication type by default when you enable the toggle for the first time.
Upload the p8 key and fill in all the required details.
Select the APNs push mode (Development/Production).
Click on Save & Publish to save the changes.
Certificate-based method (.p12)
You need to generate certificates for APNS on Apple's portal that you can later provide to Helpshift. This lets Helpshift send push notifications to your users. Apple has moved away from old type of certificates to Apple Push Notification service SSL. There is another option to create Apple Push Notification Authentication Key, but Helpshift does not support this option yet. It's also possible that you still have the old type of certificate that has not yet expired, this is also supported by Helpshift.
Apple provides two variations of Apple Push Notification service SSL
- Apple Push Notification service SSL (Sandbox)
- Apple Push Notification service SSL (Sandbox & Production)
After creating your certificate, download it. Double click on it to import it to the Keychain Access application. In the Keychain Access application, right click on the certificate that was just added, and click export it in .p12 format. Please provide a password while exporting the certificate since we do not accept empty passwords. (Note that if your development private key is not present in Keychain Access, you will not be able to export it in .p12 format.)
After export, login and upload the .p12 file in your app in the Helpshift admin panel. Provide the same password you used while exporting to .p12 format.
Please note that you need to use the same bundle identifier in the app as the one you used to create the APNS certificate.
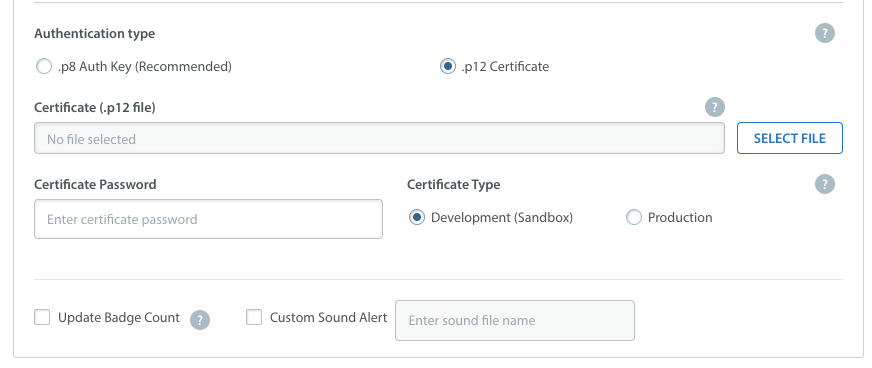
You can configure whether to send a badge or not, and sound alerts if you provided custom sounds bundled with your app to handle notifications. Save it and you're all set.
Development (Sandbox) mode vs. Production mode
When you build and run your app from Xcode, it is in development (Sandbox) mode. To test push notifications from Helpshift in this mode make sure you choose 'Development Mode' while uploading either of the above two certificate types.
When you publish your app and download from App Store, your app is in Production mode. To test push notifications from Helpshift in production mode make sure you choose 'Production Mode' while uploading a certificate of 'Apple Push Notification service SSL (Sandbox & Production)' type. Sandbox mode certificate will not work on a production environment.
We do not support using the same certificate for both sandbox and production apps. In these cases we recommend you create two separate apps on our dashboard, one in 'Production mode' and the other in 'Development mode'. While testing please use the credentials of the developement mode app. When you are ready to publish, please replace the credentials with those of the production level app.
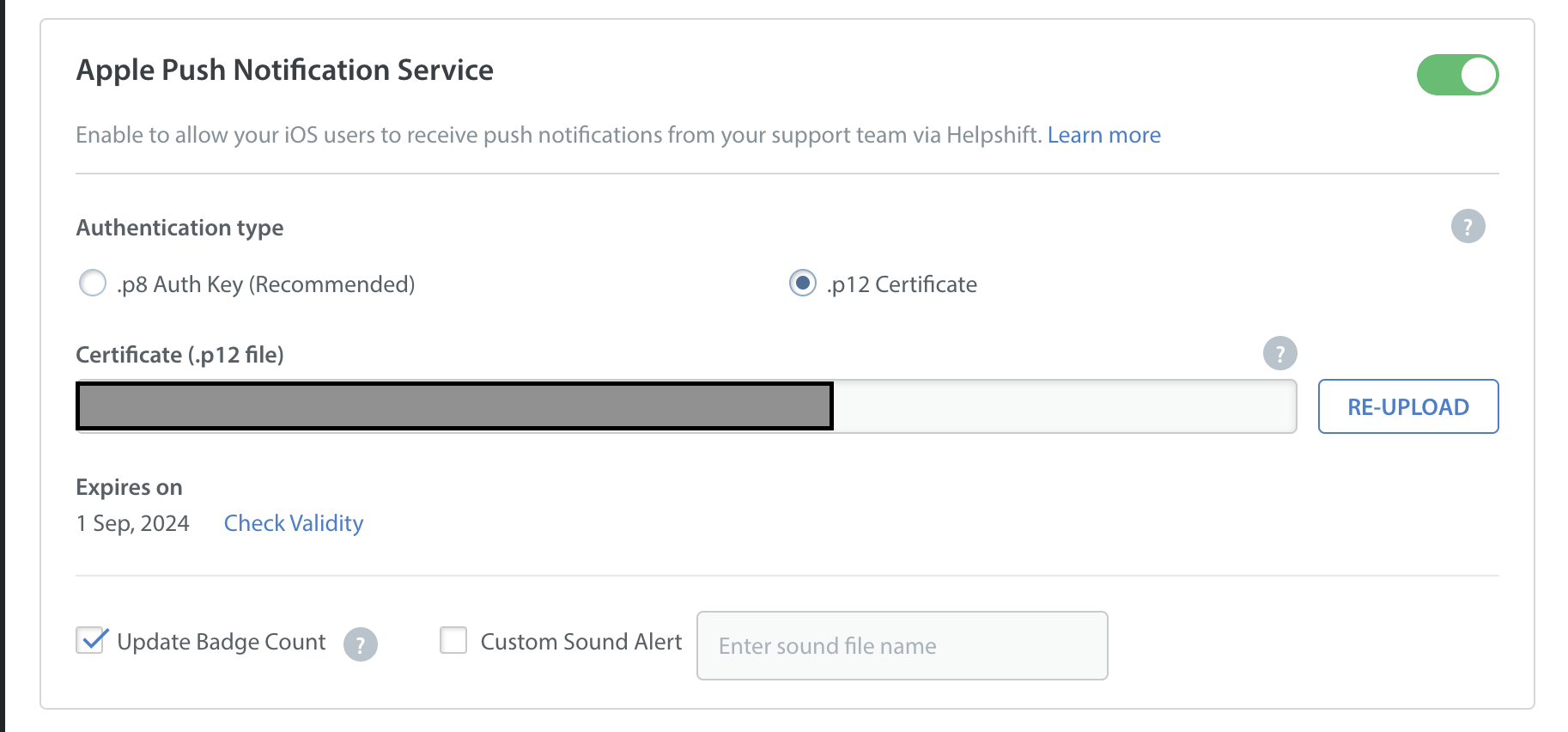
Your Push Certificate has an expiry date, as indicated in the below screenshot. Helpshift will not send you a reminder when your Push Certificate expires, so please make sure that your developer keeps a tab on the expiry date to reupload the Push Certificate.
Configure the Helpshift iOS SDK to handle notifications
When push is not configured, Helpshift SDK shows out-of-the-box "in-app notifications" for every message sent by Agents/Bots.
You should call registerDeviceToken API only after you have configured the Helpshift dashboard for push notifications. Calling the registerDeviceToken API without configuring the Helpshift dashboard will stop showing out-of-the-box "in-app notifications" for the end users.
Request notification permission and register your app for push
If your app does not already use push, you will need to enable push for your app. To enable push notification in your application you need to add notification permission request and push registration code in your AppDelegate's application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method:
- Objective-C
- Swift
- (BOOL) application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
UNUserNotificationCenter *center = [UNUserNotificationCenter currentNotificationCenter];
center.delegate = self;
[center requestAuthorizationWithOptions:(UNAuthorizationOptionBadge | UNAuthorizationOptionSound | UNAuthorizationOptionAlert)
completionHandler:^(BOOL granted, NSError *_Nullable error) {
if(!granted) {
NSLog(@"Notification auth denied");
} else {
NSLog(@"Notification auth granted");
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[UIApplication.sharedApplication registerForRemoteNotifications];
});
}
}];
}
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions options: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey : Any]? = nil) -> Bool {
let center = UNUserNotificationCenter.current()
center.delegate = self
center.requestAuthorization(options: [.badge,.alert,.sound]) { granted, error in
if granted {
print("Notification auth granted")
DispatchQueue.main.async {
UIApplication.shared.registerForRemoteNotifications()
}
} else {
print("Notification auth denied")
}
}
}
Pass registered push token to Helpshift
For Helpshift SDK to work with the Helpshift push notification service
you will need to invoke the registerDeviceToken: api call inside the application delegate method
application:didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken:
In your app delegate file it will look something like this:
- Objective-C
- Swift
- (void) application:(UIApplication *)application didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken:(NSData *)deviceToken {
[Helpshift registerDeviceToken:deviceToken];
}
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken deviceToken: Data) {
Helpshift.registerDeviceToken(deviceToken)
}
Implement push delegates
To respond to the delivery of notifications, you must implement a delegate for the shared UNUserNotificationCenter object. Your delegate object must conform to the UNUserNotificationCenterDelegate protocol, which the notification center uses to deliver notification information to your app:
- If a notification arrives while your app is in the foreground, UNUserNotificationCenterDelegate's
userNotificationCenter:willPresentNotification:withCompletionHandler:is called. - If a notification arrives while your app is in background or terminated, the system does not call the
userNotificationCenter:willPresentNotification:withCompletionHandler:method. Instead, the system alerts the user according to the information in the notification itself. - When the user selects an action from the notification interface, the system notifies your app of the user's choice. To receive responses, your delegate object must implement the
userNotificationCenter:didReceiveNotificationResponse:withCompletionHandler:method.
In both cases, you should check the "origin" field of the notification dictionary and call the corresponding SDK APIs (mentioned below) if the origin is "helpshift". The Helpshift SDK will handle the notification transparently depending on it's payload:
- For notifications sent in response to agent replies on user's support conversations, the SDK will open the corresponding conversation.
- For proactive engagement notifications, the SDK will perform the dashboard configured action.
Push delegate when app is in foreground
For the userNotificationCenter:willPresentNotification:withCompletionHandler: delegate, invoke the handleForegroundNotification:withCompletionHandler: SDK API -
- Objective-C
- Swift
- (void) userNotificationCenter:(UNUserNotificationCenter *)center
willPresentNotification:(UNNotification *)notification
withCompletionHandler:(void (^)(UNNotificationPresentationOptions)) completionHandler {
NSDictionary *userInfo = notification.request.content.userInfo;
if([@"helpshift" isEqualToString:userInfo[@"origin"]]) {
[Helpshift handleForegroundNotification:userInfo withCompletionHandler:completionHandler];
} else {
completionHandler(UNNotificationPresentationOptionBanner |
UNNotificationPresentationOptionSound |
UNNotificationPresentationOptionList);
}
}
func userNotificationCenter(
_ center: UNUserNotificationCenter,
willPresent notification: UNNotification,
withCompletionHandler completionHandler: @escaping (UNNotificationPresentationOptions) -> Void
) {
let userInfo = notification.request.content.userInfo
if let origin = userInfo["origin"] as? String, origin == "helpshift" {
Helpshift.handleForegroundNotification(userInfo, withCompletionHandler: completionHandler)
} else {
completionHandler([.banner, .sound, .list])
}
}
Push delegate when app is in background or not running
For the userNotificationCenter:didReceiveNotificationResponse:withCompletionHandler delegate, invoke the handleBackgroundNotificationClick:withCompletionHandler: SDK API -
The completion handler provided by
userNotificationCenter(_:didReceive:withCompletionHandler:)
must be invoked on the main thread.
Invoking it from a background thread can result in
NSInternalInconsistencyException crashes, especially when the app is
launched from a background or killed state.
- Objective-C
- Swift
- (void) userNotificationCenter:(UNUserNotificationCenter *)center
didReceiveNotificationResponse:(UNNotificationResponse *)response
withCompletionHandler:(void (^)(void))completionHandler {
NSDictionary *userInfo = response.notification.request.content.userInfo;
if([@"helpshift" isEqualToString:userInfo[@"origin"]]) {
[Helpshift handleBackgroundNotificationClick:userInfo
withCompletionHandler:^{
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completionHandler();
});
}];
} else {
completionHandler();
}
}
func userNotificationCenter(
_ center: UNUserNotificationCenter,
didReceive response: UNNotificationResponse,
withCompletionHandler completionHandler: @escaping () -> Void
) {
let userInfo = response.notification.request.content.userInfo
if let origin = userInfo["origin"] as? String, origin == "helpshift" {
Helpshift.handleBackgroundNotificationClick(userInfo) {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
completionHandler()
}
}
} else {
completionHandler()
}
}
Configure NotificationService extension
Your app only needs to configure the NotificationService extension if you are using Proactive Engagement feature. For support notifications, you can skip this configuration.
If you are using Helpshift's Proactive Engagement feature, you will need to add a NotificationService extension to your app. This extension lets the app intercept the notification and modify it's payload before iOS system posts the notification in system tray. For more details on what this service extension does and how to configure it in your app, you can refer the Apple documentation.
Helpshift uses this extension to download images to display in the push notification. If your app already has a NotificationService extension, you can re-use it for handling Helpshift notifications. In the didReceiveNotificationRequest:withContentHandler: method of your notification service, call the corresponding Helpshift API -
- Objective-C
- Swift
- (void) didReceiveNotificationRequest:(UNNotificationRequest *)request
withContentHandler:(void (^)(UNNotificationContent *content))contentHandler {
NSString *origin = request.content.userInfo[@"origin"];
if([@"helpshift" isEqualToString:origin]) {
[Helpshift handleBackgroundNotification:request
withContentHandler:contentHandler];
} else {
contentHandler(request.content);
}
}
override func didReceive(
_ request: UNNotificationRequest,
withContentHandler contentHandler: @escaping (UNNotificationContent) -> Void
) {
let origin = request.content.userInfo["origin"] as? String
if origin == "helpshift" {
Helpshift.handleBackgroundNotification(request, withContentHandler: contentHandler)
} else {
contentHandler(request.content)
}
}
In-app notifications
In-app notifications are similar to Apple's push notification banners. Unlike push notifications, they appear within your app when it is in use by the user. The UI for these notifications looks like this -
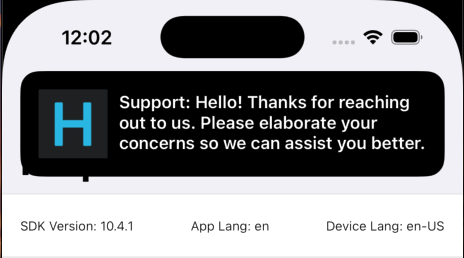
These notifications are sent in following cases -
- An agent replies to a customer's issue. Your customers can click on these banners to go straight into the conversation screen.
- The user receives a Proactive Engagement notification of In-App type while they are actively using your app. Clicking the banner will perform the action you have configured for the notification on admin dashboard.
Enabling/Disabling In-app notifications
This section is applicable only for support in-app notifications, not for proactive engagement notifications.
You can enable/disable support in-app notifications using the enableInAppNotification flag in the Helpshift install call.
| Flag | enableInAppNotification |
| Values | YES/NO |
| Default | YES |
The default value of this flag is YES i.e support in-app notifications will be enabled.
Example:
- Objective-C
- Swift
NSDictionary *config = @{ @"enableInAppNotification": @YES };
[Helpshift installWithPlatformId:@"YOUR_PLATFORM_ID"
domain:(NSString *)domain
config:@"YOUR_DOMAIN" config:config];
let config = ["enableInAppNotification" : true]
Helpshift.install(withPlatformId: "YOUR_PLATFORM_ID", domain: "YOUR_DOMAIN", config: config)
Pausing In-app notifications
Use the API pauseDisplayOfInAppNotification to pause/resume the notifications. When YES is passed to this method, display of in-app notifications is paused even if they arrive. When you pass NO, the in-app notifications start displaying. Note that if you have disabled support in-app notifications, this flag will have no effect for support notifications. It will still work for proactive engagement in-app notifications.
Example:
- Objective-C
- Swift
[Helpshift pauseDisplayOfInAppNotification:YES]; // To temporarily pause in-app notifications
[Helpshift pauseDisplayOfInAppNotification:NO]; // To resume showing the in-app notifications
Helpshift.pauseDisplayOf(inAppNotification: true) // To temporarily pause in-app notifications
Helpshift.pauseDisplayOf(inAppNotification: false) // To resume showing the in-app notifications
Notification badges
If you want to show your user notifications for replies you send to the
issues they posted, you can use notification counts provided by
Helpshift SDK that gives you the total number of unread messages and
display it as a badge. You can get notification counts asynchronously by
implementing the HelpshiftDelegate in your respective .h and .m
files. Notifications are typically displayed as badges
inside your app where a user invokes the help section. These badges can
be displayed anywhere in your app's interface to tell the user that they
have unread replies/messages from you. For example to display a badge on
a view (lets say its called yourView which can set its textLabel) while
you are polling for notifications using:
[Helpshift requestUnreadMessageCount:YES];
You can implement something like the following in the notification count delegate method:
- Objective-C
- Swift
- (void) handleHelpshiftEvent:(NSString *)eventName withData:(NSDictionary *)data {
...
if([eventName isEqualToString:HelpshiftEventNameReceivedUnreadMessageCount]) {
int count = [data[HelpshiftEventDataUnreadMessageCount] intValue];
BOOL fromCache = [data[HelpshiftEventDataUnreadMessageCountIsFromCache] boolValue];
NSLog(@"Unread count: %d", count);
NSLog(@"Is unreadCount served from local cache : %d", fromCache);
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[yourView setTextLabel:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d",count];
});
}
}
func handleHelpshiftEvent(_ eventName: String, withData data: [AnyHashable : Any]?) {
if eventName == HelpshiftEventNameReceivedUnreadMessageCount {
guard let data = data else { return }
let count = data[HelpshiftEventDataUnreadMessageCount] as? Int
let isFromCache = data[HelpshiftEventDataUnreadMessageCountIsFromCache] as? Bool
print("Count: \(count), fromCache: \(isFromCache)")
DispatchQueue.main.async {
yourLabel.text = "\(count)"
}
}
}
Similarly for a UITabBarItem in the notification count delegate method
you can implement something like:
- Objective-C
- Swift
- (void) handleHelpshiftEvent:(NSString *)eventName withData:(NSDictionary *)data {
...
if([eventName isEqualToString:HelpshiftEventNameReceivedUnreadMessageCount]) {
int count = [data[HelpshiftEventDataUnreadMessageCount] intValue];
BOOL fromCache = [data[HelpshiftEventDataUnreadMessageCountIsFromCache] boolValue];
NSLog(@"Unread count: %d", count);
NSLog(@"Is unreadCount served from local cache : %d", fromCache);
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
tabBarItem.badgeValue = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d",count];
});
}
}
func handleHelpshiftEvent(_ eventName: String, withData data: [AnyHashable : Any]?) {
if eventName == HelpshiftEventNameReceivedUnreadMessageCount {
guard let data = data else { return }
let count = data[HelpshiftEventDataUnreadMessageCount] as? Int
let isFromCache = data[HelpshiftEventDataUnreadMessageCountIsFromCache] as? Bool
print("Count: \(count), fromCache: \(isFromCache)")
DispatchQueue.main.async {
tabBarItem.badgeValue = "\(count)"
}
}
}
These will update your view or UITabBarItem whenever a new notification
arrives in the delegate method. The situation can vary depending upon
your app UI. Showing notification counts at appropriate places would help
you draw in your users so that you can engage them more in conversations
and hence solve their problems better. To display the notification
count of unread messages stored locally to your users, you can call requestUnreadMessageCount:
- Objective-C
- Swift
[Helpshift requestUnreadMessageCount:NO]
Helpshift.requestUnreadMessageCount(false)
to retrieve the unread messages count stored locally and display the unread count similar to mentioned in the above examples.
Refer Unread Message Count Event for knowing more on how the SDK notifies of the unread count to your app.
Reset badge count
If you need to handle badge reset in the application icon, you can do
something like below in the applicationDidBecomeActive: delegate
method:
- (void)applicationDidBecomeActive:(UIApplication *)application
{
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] setApplicationIconBadgeNumber:0];
}