Notifications
Notifications
Configure Push notifications and in-app notifications
Push notifications via Helpshift
Helpshift allows you to send Push notifications when an agent replies to a conversation.
Prerequisites
Implement FCM (or the older GCM) push in your app.
For FCM, refer to the Firebase Cloud Messaging documentation.
For GCM, refer to the Google Cloud Messaging documentation.
During this, you can also refer to the following sample apps which enable the Helpshift Android SDK to handle push notifications -
| FCMClient | implement FCM Push in your app along with helpshift support. |
| GcmClient | implement GCM Push (using Google Play Services) in your app along with helpshift support. This is a port of GcmClient project from Gradle to Ant build system. |
| GCMApp (Deprecated) | implement GCM Push in your app along with helpshift support. |
Configure Helpshift Agent Dashboard
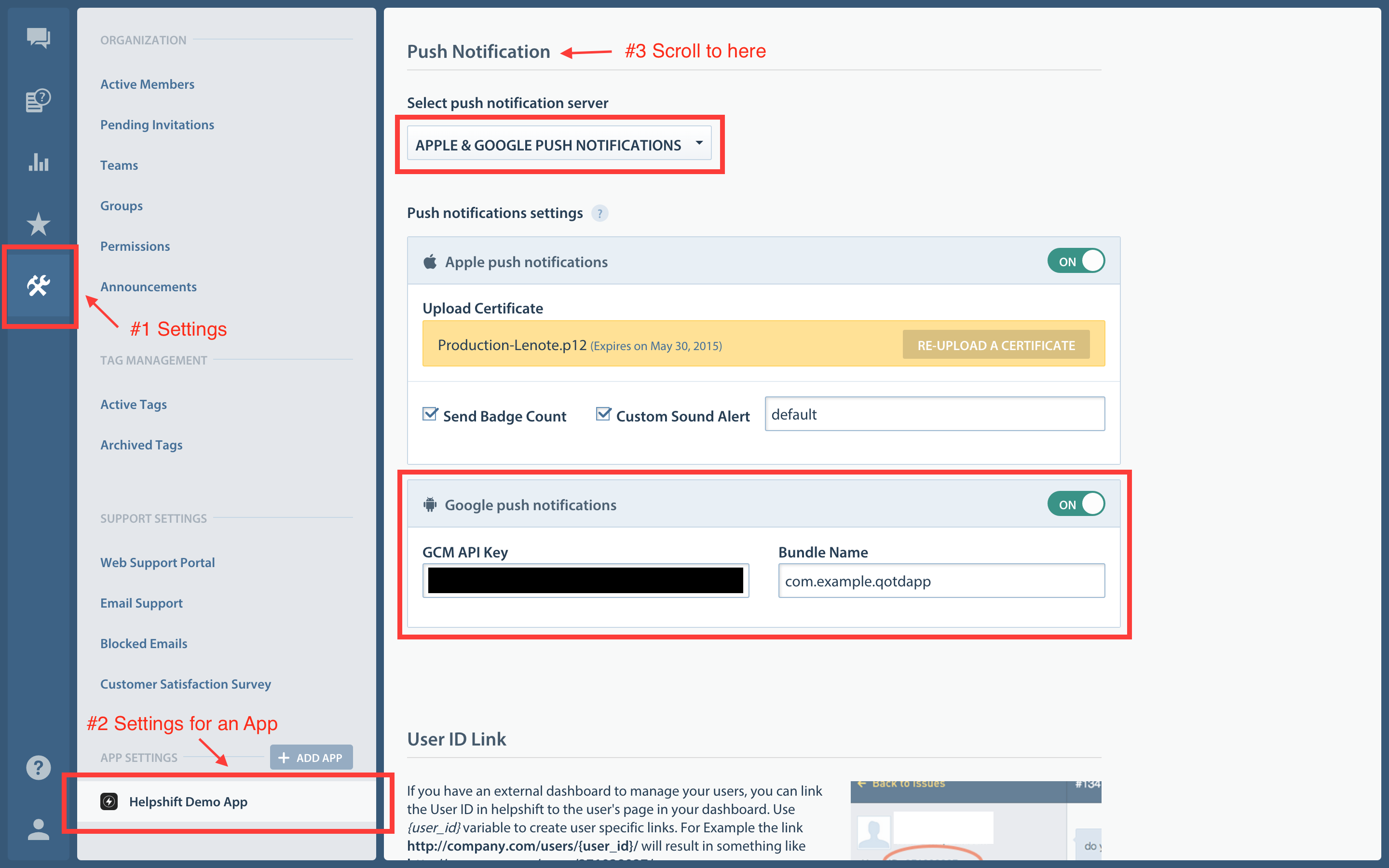
To enable the Helpshift system to send push notifications to your users you will have to add your GCM Key and Bundle Name via the helpshift admin interface.
Enter your Google Push notifications credentials per app, via the Settings page > App listing in the left navigation > Scroll down to Push Notifications settings section for the app.
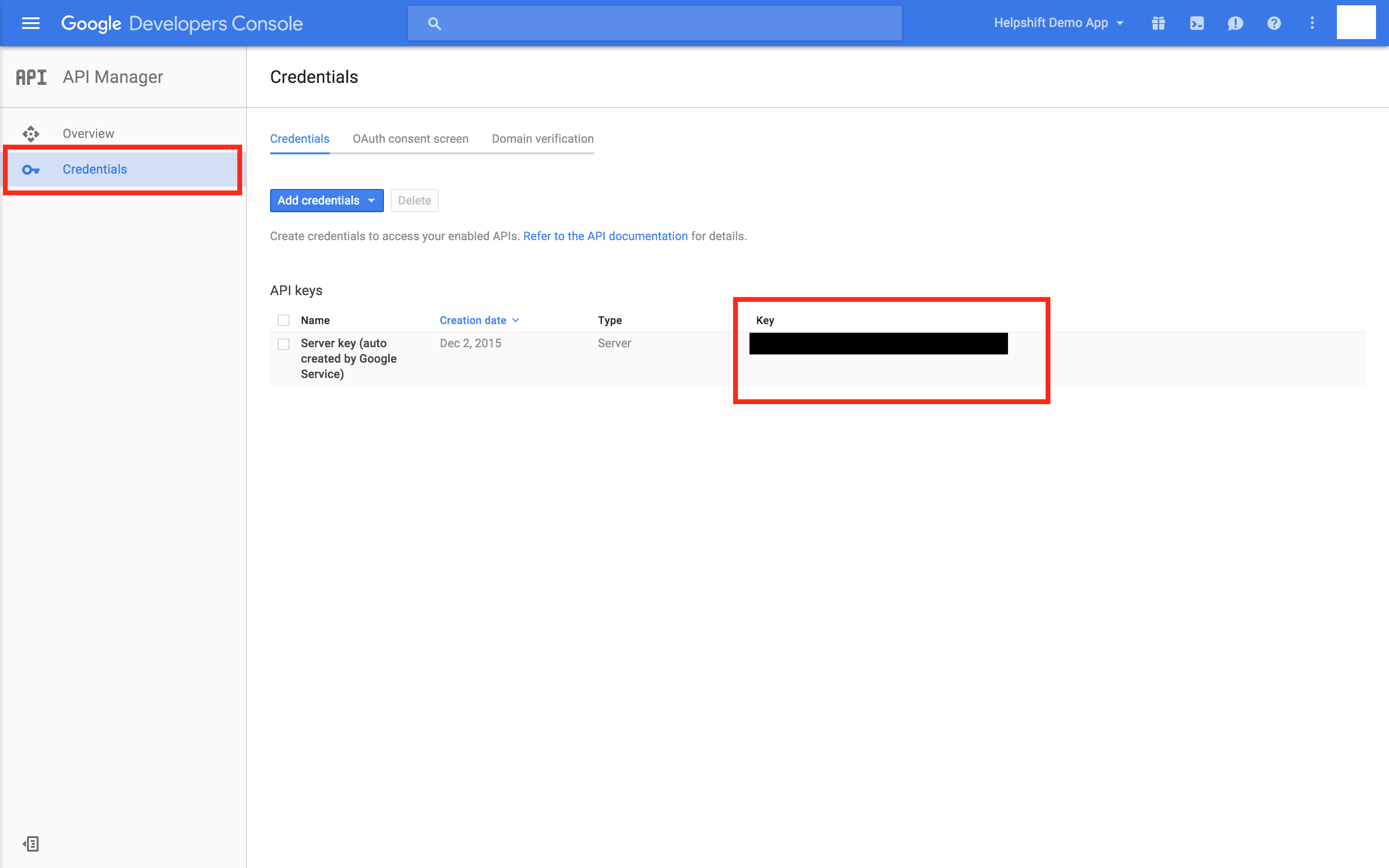
For GCM users, the API key can be found at your Google API Console
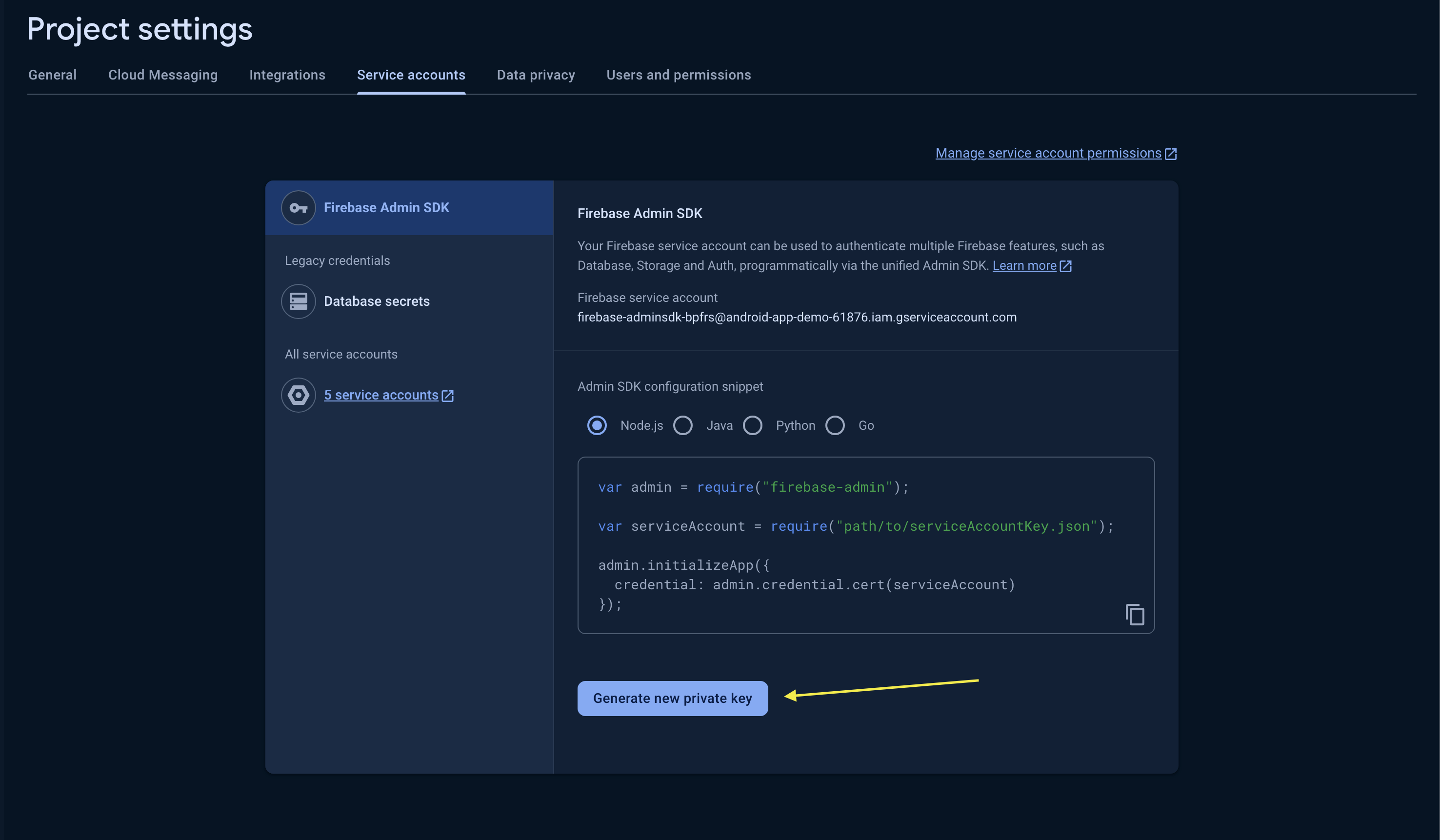
And for FCM users, the API key can be found at your Firebase API Console
Configure Helpshift Android SDK
- Applicable to SDK v3.0.0 & above
- When push is not configured, Helpshift SDK shows out-of-the-box "in-app notifications" for every message sent by Agents/Bots.
You should call
registerDeviceTokenAPI only after you have configured the Helpshift dashboard for push notifications. Calling theregisterDeviceTokenAPI without configuring the Helpshift dashboard will stop showing out-of-the-box "in-app notifications" for the end users.
- Send the device registration id to Helpshift via the
Core.registerDeviceTokenAPI
private void sendRegistrationIdToBackend() {
// Send registrationId to Helpshift
Core.registerDeviceToken(context, regid);
}
- Inside your "GcmBroadcastReceiver's
onReceivemethod" check origin is "helpshift" and pass the intent toCore.handlePushAPI
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if(intent.getExtras().getString("origin").equals("helpshift")) {
Core.handlePush(context, intent);
}
// Explicitly specify that GcmIntentService will handle the intent.
ComponentName comp = new ComponentName(context.getPackageName(),
GcmIntentService.class.getName());
// Start the service, keeping the device awake while it is launching.
startWakefulService(context, (intent.setComponent(comp)));
setResultCode(Activity.RESULT_OK);
}
- If you are using GCM service which provides "Bundle" argument instead of Intent, you should use
Core.handlePushAPI which takes Bundle argument.
@Override
public void onMessageReceived(String from, Bundle data) {
String origin = data.getString("origin");
if (origin != null && origin.equals("helpshift")) {
Core.handlePush(this, data);
}
}
- If you are using FCM's new
FirebaseMessagingServicewhich provides "RemoteMessage" argument, you should useCore.handlePushAPI which takes a Map argument.
@Override
public void onMessageReceived(RemoteMessage message) {
Map<String, String> data = message.getData();
String origin = data.get("origin");
if (origin != null && origin.equals("helpshift")) {
Core.handlePush(this, data);
}
}
In-app notifications
In-app notifications are similar to notifications in the notification drawer . Unlike push notifications, they appear only when you app is running.
These notifications are sent when an agent replies to a customer's issue. Your customers can go straight into the conversation screen when they tap on the notification.
If the GCM/FCM device token is registered for push notifications, then in-app notifications will be disabled. In-app notifications are disabled to avoid duplicate notifications from both push notifications and in-app notifications.
Customizing notification icons
By default the application icon is used as the notification icon. You can customize the notification icons using the config in the install call.
- Using InstallConfig
- Using Map
InstallConfig installConfig = new InstallConfig.Builder()
.setNotificationIcon(R.drawable.notification_icon_small)
.setLargeNotificationIcon(R.drawable.notification_icon_large)
.build();
Core.install(this, // "this" should be the application object
"<YOUR_API_KEY>",
"<YOUR_COMPANY>.helpshift.com",
"<YOUR_APP_ID>",
installConfig);
HashMap config = new HashMap();
config.put("notificationIcon", R.drawable.notification_icon_small);
config.put("largeNotificationIcon", R.drawable.notification_icon_large);
Core.install(this, // "this" should be the application object
"<YOUR_API_KEY>",
"<YOUR_COMPANY>.helpshift.com",
"<YOUR_APP_ID>",
config);
Customizing notification sound
Available from SDK version 3.7.2 and above.
Starting from SDK v7.4.0, the sound provided here would only be set for the default notification channel that the SDK creates on its own on Android OS 8.0 & above. This sound can only be set once on the default channel and it won’t change if a different sound resource is passed.
If the sound needs to be changed later on, it is recommended to create your own notification channels. Refer this.
By default the default device notification sound is used for helpshift notifications. You can customize the notification sound using the config in the install call.
For example:
- Using InstallConfig
- Using Map
InstallConfig installConfig = new InstallConfig.Builder()
.setNotificationSound(R.raw.notification_sound)
.build();
Core.install(this, // "this" should be the application object
"YOUR_API_KEY",
"<YOUR_HELPSHIFT_DOMAIN>.helpshift.com",
"YOUR_APP_ID",
installConfig);
HashMap config = new HashMap();
config.put("notificationSound", R.raw.notification_sound);
Core.install(this, // "this" should be the application object
"YOUR_API_KEY",
"<YOUR_HELPSHIFT_DOMAIN>.helpshift.com",
"YOUR_APP_ID",
config);
Customizing notification channels
Available from SDK version 6.2.0 and above
Starting from Android Oreo, Helpshift notifications will create a default channel named In-app Support. If you want to customize the name and description for the default channel, you can do so by using the following resources in your strings.xml file:
<string name="hs__default_notification_channel_name">Example Support Name</string>
<string name="hs__default_notification_channel_desc">Example Support Description</string>
If you want to customize the notification channels, you can create your own custom channels and provide their channel IDs using the following config API:
supportNotificationChannelId
For example:
- Using InstallConfig
- Using Map
InstallConfig installConfig = new InstallConfig.Builder()
.setSupportNotificationChannelId("SUPPORT_CHANNEL_ID")
.build();
Core.init(Support.getInstance());
Core.install(this, // "this" should be the application object
"<YOUR_API_KEY>",
"<YOUR_COMPANY>.helpshift.com",
"<YOUR_APP_ID>",
installConfig);
HashMap config = new HashMap();
config.put("supportNotificationChannelId", "SUPPORT_CHANNEL_ID");
Core.init(Support.getInstance());
Core.install(this, // "this" should be the application object
"YOUR_API_KEY",
"<YOUR_HELPSHIFT_DOMAIN>.helpshift.com",
"YOUR_APP_ID",
config);
Configuring in-app notifications
If you do not want the in-app notification support provided by the Helpshift SDK, you can set the flag to false. The default value of this flag is true i.e., in app notification will be enabled.
Flag:enableInAppNotificationValues:true/falseDefault:true
Example:
- Using InstallConfig
- Using Map
InstallConfig installConfig = new InstallConfig.Builder()
.setEnableInAppNotification(true)
.build();
Core.install(this, // "this" should be the application object
"<YOUR_API_KEY>",
"<YOUR_COMPANY>.helpshift.com",
"<YOUR_APP_ID>",
installConfig);
Hashmap config = new HashMap();
config.put("enableInAppNotification", true);
Core.install(this, // "this" should be the application object
"<YOUR_API_KEY>",
"<YOUR_COMPANY>.helpshift.com",
"<YOUR_APP_ID>",
config);
Showing notification count when replies are sent to the user
Fetching notification count can be done in two ways.
Synchronous fetch notification count
- If you want to show your user notifications for replies on the issues posted, you can get the notification count synchronously from cache. Example:-
Integer notifCount = Support.getNotificationCount();
Asynchronous fetch notification count
- If you want to show your user notifications for replies on the issues
posted, you can get the notification count asynchronously by
implementing the
countHandlerandfailHandler. Example:-
Support.getNotificationCount(countHandler, failHandler);
- The notification count can be obtained from the message recived though the countHandler. Example:-
private Handler countHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
Bundle countData = (Bundle) msg.obj;
Integer count = countData.getInt("value");
Boolean cache = countData.getBoolean("cache");
if (cache) {
Log.d("Notification Count", "local" + count);
} else {
Log.d("Notification Count", "server" + count);
}
}
};
- The notification count is fetched via this API from the SDK cache and Helpshift's servers (indicated by the value of
cachein the example above). However, the count from Helpshift’s servers is rate limited and it returns the value only if a subsequent call is made to the API, after the reset timeout or when the user just closes the chat screen (whichever is earlier). For an active issue, the reset timeout is 1 minute and 5 minutes for inactive issues.