Proactive Engagement
Proactive Engagement lets you reach out to your players by sending Push/In app Notifications on their mobile devices and engage in various ways including starting conversations.
Note
- This feature is available from SDK X 10.5.0 onwards.
- All the public APIs in the SDK should be called after initializing the SDK via Helpshift.install() API
- Before starting with Proactive Engagement, please ensure that you have integrated push notifications with Helpshift SDK. Please refer Notifications section for integration guide.
- Please note that the SDK does not ask for posting notifications permission for client application. For Proactive Engagement, you need to ask for the POST_NOTIFICATION permission yourself.
Configuring Proactive Engagement notifications
To publish a notification follow these steps:
- Open the Helpshift Dashboard and navigate to Settings > Workflows > Proactive Engagement
- Create a notification for the app you want with either Push or In-App type notification
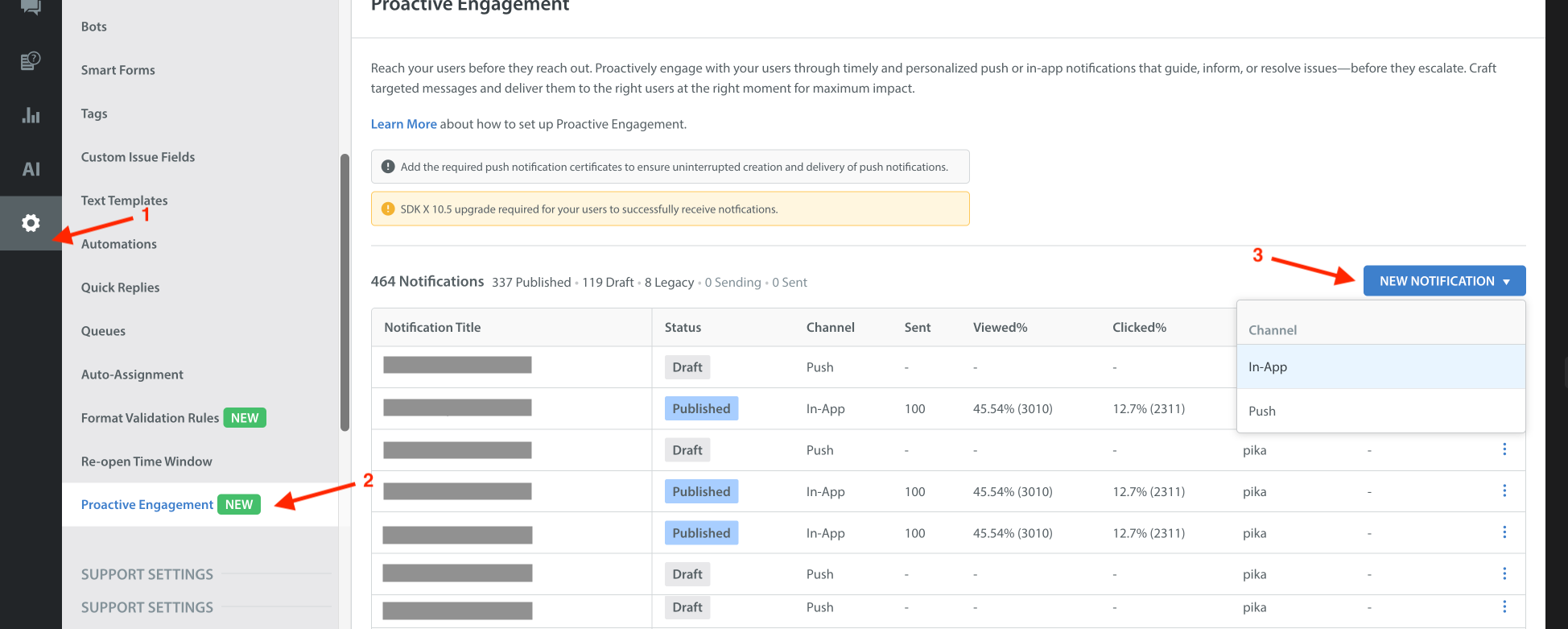
- Select the desired action from available options, fill up the notification content and add context as per your needs.
- Intents/CIFs/tags/initial message etc configured here will be used when the end user starts a conversation by clicking on the notification.
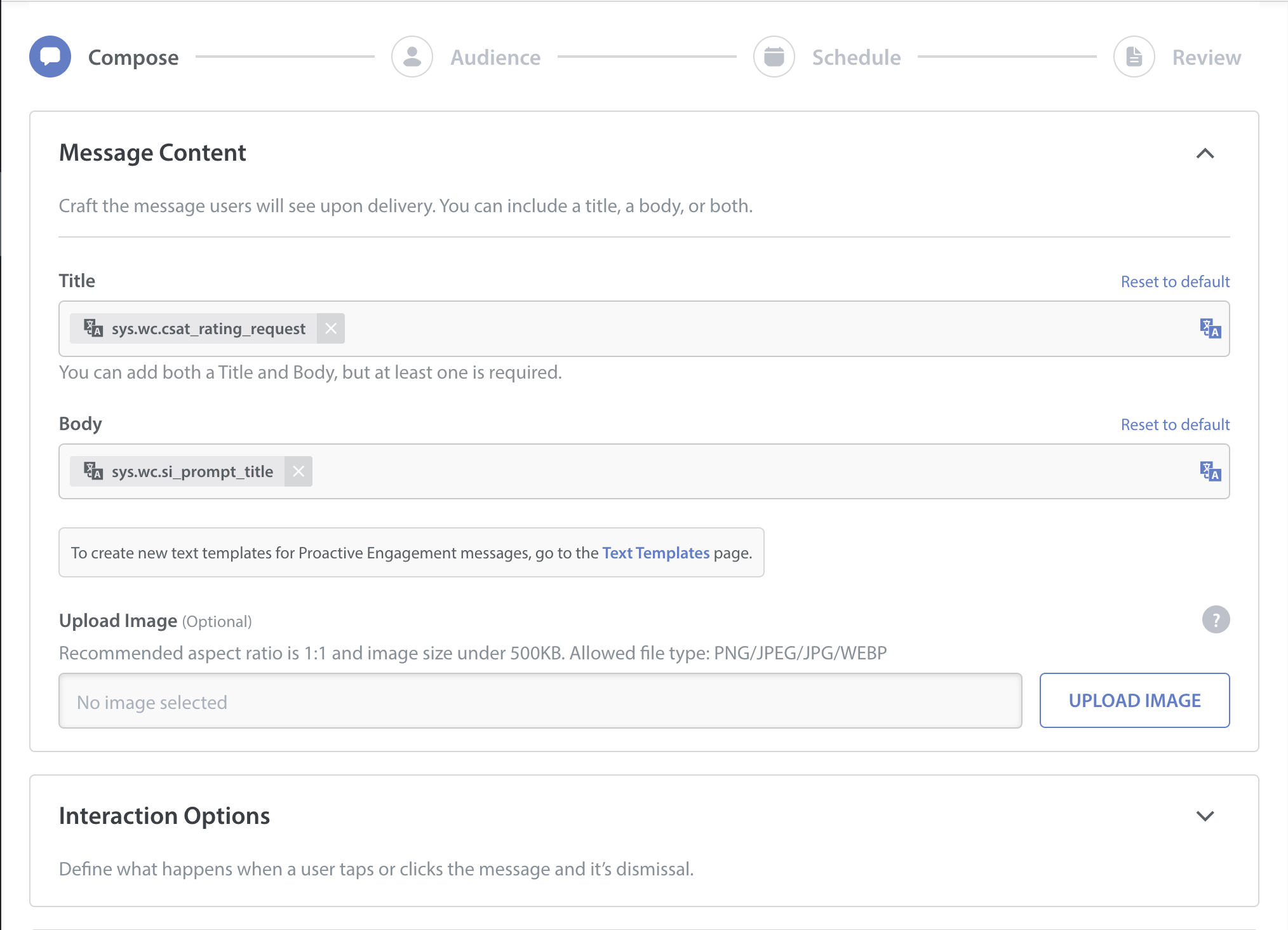
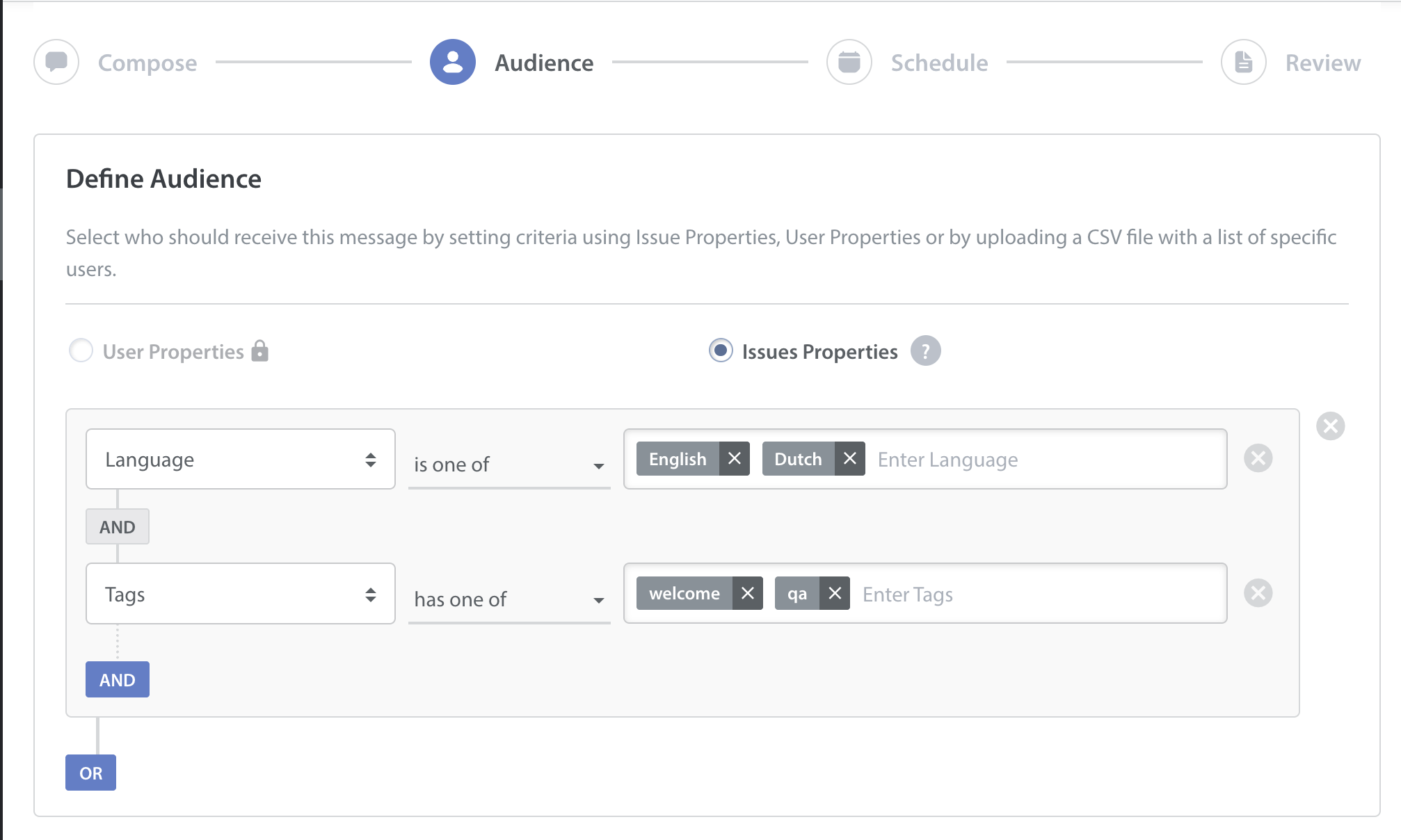
- Configure the audience filter that you want to target. You can filter the audience based on:
- Issue properties
- User properties using User Hub integration
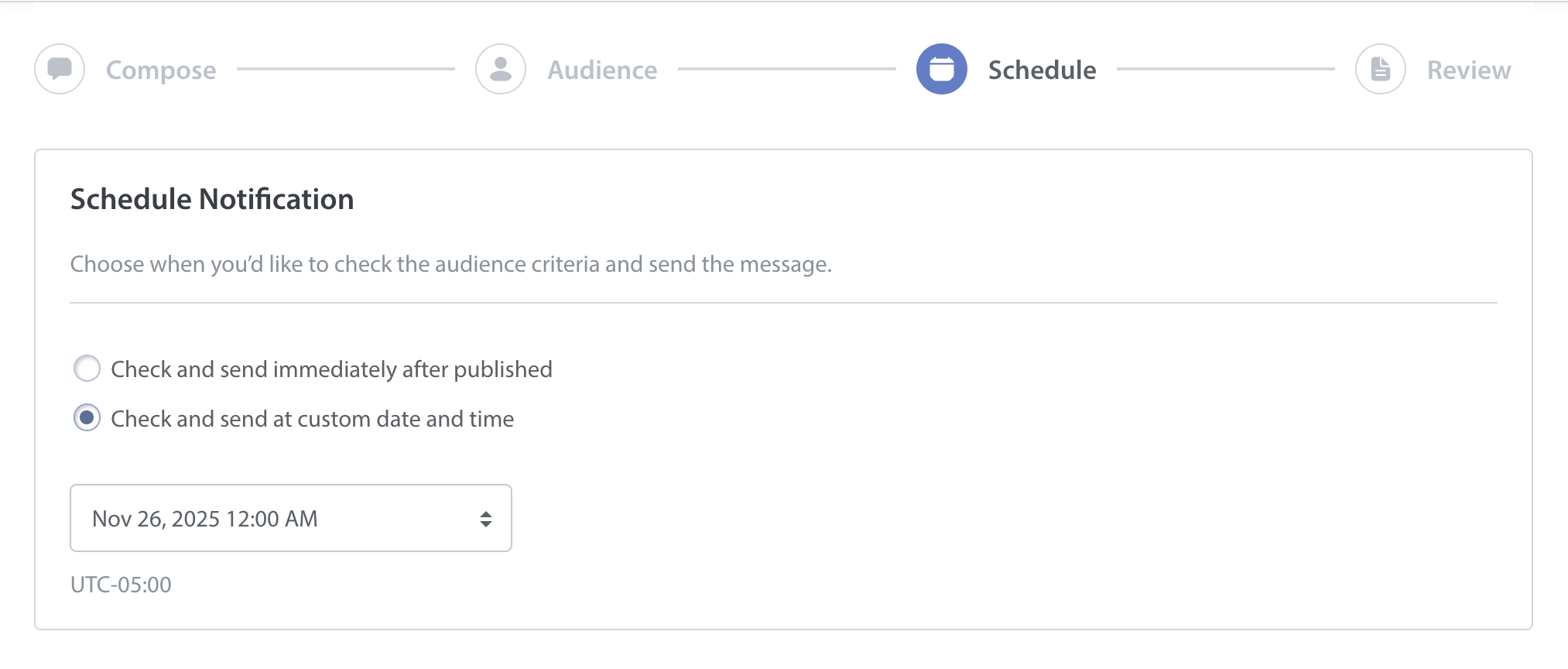
- Schedule the notification. You will get a chance to review the full configuration before publishing the notification.
Push notifications
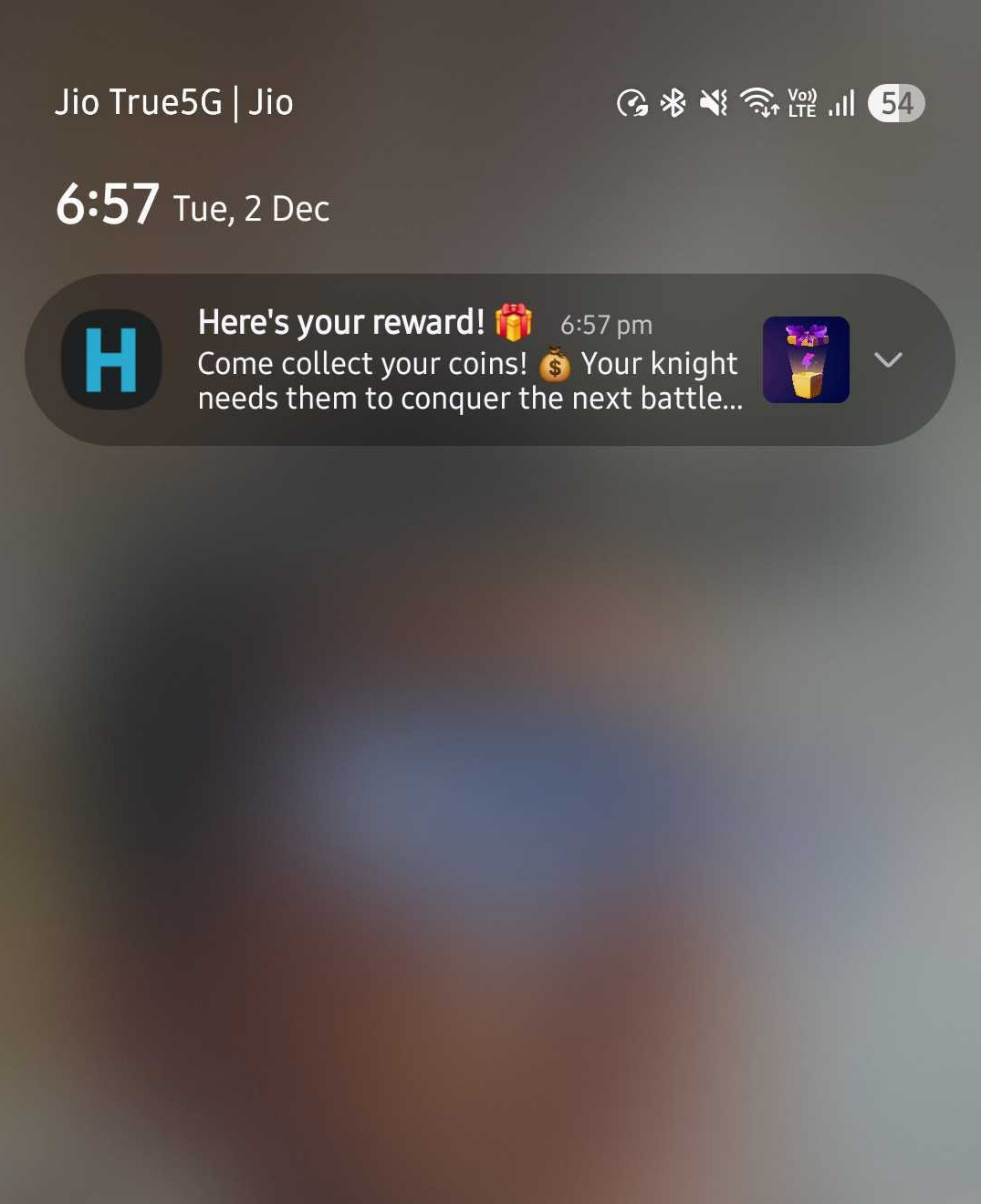
- Push type notifications will be shown in the Notification tray of the device.
- Use this type of notification when you want to re-engage the user who has not been active or grab attention of users with some interesting information.
- With the various actions available on click of the notification or the buttons in the notification, you can redirect the user to any part of your application via deeplinks (need to be setup by the client application) or start a conversation via “Start Chat“ option or redirect them to an FAQ for quick help.
- Push notifications will show up even if the app is not running in background.
- Rich text is supported in the content of the notification. Make sure you provide compatible/supported HTML content used for setting up the notification on Dashboard.
- Due to system limitations, rich text in notifications is not supported from Android 16 unless Android fixes it.
In-App notifications

- InApp notifications are used to grab attention of the user who is already using your application, is on the application UI and you want to alert/engage them.
- If the user is not currently using the app, we show the in-app notification when the application is opened next time. This way an in-app notification is not lost even if user is not on the application screen.
- We currently support Banner type notifications with click actions similar to Push notifications.
- Note:
- If the SDK receives multiple in-app notifications when the app was in background then the SDK will show only the latest received in-app notification and discard all the older ones.
- By default, In-App notifications expire in 2 days from the time of delivery to the device. If in-app received in background expires, then SDK will not show the expired in-app notification.
Delegate push notification to Helpshift SDK
- Integrating handling of Proactive Engagement notification requires no extra effort if push notification were already integrated for Helpshift SDK messages.
- Refer Push Notifications integration page.
Setting defaults for notification properties
- If you need to set some defaults to be used in proactive notifications then you can use this API. We recommend to call this API right after
Helpshift.install()call. - Following configurations are available via this api
notificationIconId: Android resource id, integer value, for small icon to be used for proactive notification. If not configured then app icon will be used by default.largeNotificationIconId: Android resource id, integer value, for large notification image. This will be used when an image is not configured in the notification on Dashboard.soundId: Android resource id, integer value, for the sound to be used for proactive notification. If not provided then system default sound will be used. Note that this sound will be associated with the default notification channel that SDK creates for Proactive Engagement notifications. Refer below section.
Custom notification channels for Proactive Engagement notifications
- If you want to set your own notification channels (i.e these channels are created by the client application beforehand) for Proactive engagement notifications then you can pass on the values in this API.
- If the values are not set then the SDK creates default notification channel by itself.
- For proactive engagement notifications that lead to Helpcenter or Conversations will create a channel by name: “Proactive Support“
- For proactive engagement notifications that lead to user engagement will create a channel by name: “Proactive Engage“
- You can provide your own channel Ids to be used by the SDK via this API:
proactiveSupportChannelId: Channel id for Proactive support cases.proactiveEngageChannelId: Channel id for Proactive Engage cases.
| API: | Helpshift.setProactivePushNotificationDefaults() |
| Values: | Map<String, Object> |
| Min SDK | v10.5.0 |
| Should be called after | install() |
Example:
public class MainApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
// Install call
Helpshift.install(this, "<PLATFORM_ID>", "<DOMAIN>", configurations);
Map<String, Object> defaults = new HashMap<>();
defaults.put("notificationIconId", R.drawable.icon);
defaults.put("largeNotificationIconId", R.drawable.large_icon);
defaults.put("soundId", R.drawable.sound);
defaults.put("proactiveSupportChannelId", "Customer Channel name");
defaults.put("proactiveEngageChannelId", "Customer Channel name");
Helpshift.setProactivePushNotificationDefaults(defaults);
}
}
Pausing InApp notifications
- This API will pause/unpause the showing of in-app notifications to the end user when application is in foreground.
- You can use this API to pause in-app notification when you know that the user should not be disturbed. For example, the user is on app startup screen, the app is still loading, user is in game play or on a payment screen etc. In such cases you can pause the in-app notifications from Helpshift SDK and once the user is done you can unpause it via the same API.
- Note that in-app notifications received when the notifications were paused are not lost, they are shown to the user as soon as the notifications are unpaused again.
- This API needs to be called in every app session since SDK will not persist its value across sessions. The need to pause/unpause in-app notification is real time and depends on the current application state best known to the client application itself, hence the SDK does not persist the value across app sessions.
- By default the SDK will always show the in-app notifications unless explicitly paused by the client app by using this API.
shouldPauseInAppNotification: Set tofalseby default.false: Starts showing the in-app notifications, if available.true: Pauses the in-app notifications. In-app notifications received during the time, i.e when this value was true, are shown when this value is later set to false.
| API: | Helpshift.shouldPauseInAppNotification() |
| Values: | boolean |
| Min SDK | v10.5.0 |
| Should be called after | install() |
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//... Assuming Helpshift.install() is already called in Application.onCreate()
// based on state of your app, decide to pause/unpause proactive engagement notifications.
Helpshift.shouldPauseInAppNotification(true/false);
//...
}
Passing fallback configuration
- You may want to add configuration specific to the current user in your app when interacting with proactive notifications.
- This configuration is used when no configuration is provided from the Dashboard when configuring the notification. This configuration data is exactly same as we would expect in other APIs like showConversation() or showFAQs().
- We will also use this configuration for the next issue filed in the same session. For example, if the user starts a conversation via proactive engagement notification and the conversation gets resolved in the same session and the user starts another conversation then this configuration will be used for the new conversation.
- Note: You need to call this API after
Helpshift.install() API and before Helpshift.handlePush() - Implement
public interface com.helpshift.proactive.HelpshiftProactiveAPIConfigCollectorand callHelpshift.setHelpshiftProactiveConfigCollector("<instance of HelpshiftProactiveAPIConfigCollector>")method to initialize the config collector. - You will have to implement the method
getAPIConfig()where you can add any user specific config in the same format as you add in other public APIs like showConversation() or showFAQs(). HelpshiftProactiveAPIConfigCollector.getAPIConfig()is invoked by the SDK before handling the notification click action and evaluating the configuration to be used for handling the notification.- For example, following code shows how to implement HelpshiftProactiveAPIConfigCollector interface and how to add user specific configurations using getAPIConfig() method -
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements HelpshiftProactiveAPIConfigCollector {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//... Assuming Helpshift.install() is already called in Application.onCreate()
// initialise proactiveConfig collector
Helpshift.setHelpshiftProactiveConfigCollector(this);
//...
}
//...
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getAPIConfig() {
// config map
Map<String, Object> localConfig = new HashMap<>();
// set tags for tracking
localConfig.put("tags", new String[]{"currentUserTag", "currentUserLevel"});
// set custom issue fields
Map<String, Object> cifMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, String> isPro = new HashMap<>();
isPro.put("type", "boolean");
isPro.put("value", "true");
cifMap.put("is_pro", isPro);
localConfig.put("cifs", cifMap);
// ..etc
return localConfig;
}
}
Note
The "customIssueFields" key has been deprecated. We strongly recommend transitioning to using the "cifs" key as the preferred method for passing custom issue fields.